AI 환경은 단순한 챗봇에서 자율적으로 작업을 계획하고 추론하며 실행할 수 있는 AI 에이전트로 빠르게 전환되고 있습니다. 그 선두에는 도커 케이전트 - 강력하고 사용하기 쉬운 멀티 에이전트 런타임으로 전 세계 개발자를 위한 AI 에이전트 개발의 대중화를 이끌고 있습니다.
단순한 텍스트 기반 응답을 제공하는 기존의 AI 챗봇과 달리, 에이전트 AI 시스템은 다음과 같이 구축됩니다. 카젠트 는 복잡한 문제를 관리 가능한 작업으로 세분화하고, 전문 AI 에이전트에게 작업을 위임하는 동시에 모델 컨텍스트 프로토콜(MCP)을 통해 외부 도구와 API를 활용할 수 있습니다.
이 게시물에서는 자연어 쿼리를 이해하는 AI 에이전트를 설정하고, Couchbase 인스턴스와 상호 작용하여 데이터를 읽고 쓰는 방법, 그리고 카우치베이스 MCP 서버 그리고 시약을 사용하여 이 에이전트를 프로덕션에 쉽게 배송하는 방법을 알아보세요.
카젠트란 무엇인가요?
카젠트 는 사용자 정의가 가능한 오픈 소스 멀티 에이전트 런타임으로, 전문화된 도구와 기능으로 AI 에이전트 간의 상호 작용을 관리하기 위해 에이전트를 간편하게 오케스트레이션할 수 있습니다.
카젠트의 주요 기능
-
- YAML 구성: 복잡한 코딩이 필요 없는 간단한 선언적 YAML 파일을 사용하여 전체 에이전트 에코시스템을 정의하세요.
- 내장된 추론 기능: “생각하기”, “할 일”, “기억하기'와 같은 도구를 통해 세션 전반에 걸쳐 정교한 문제 해결과 맥락 유지를 가능하게 합니다.
- 여러 AI 제공업체 지원: OpenAI, Anthropic, Google Gemini, Docker Model Runner 등 여러 AI 제공업체를 지원합니다.
- 풍부한 에코시스템 지원: 상담원은 모델 컨텍스트 프로토콜(MCP)을 통해 외부 도구, API 및 서비스에 액세스할 수 있습니다.
카젠트의 작동 원리를 알아보려면 다음을 참조하세요. 공식 문서에서 README 및 사용법 파일에 저장합니다. 이 개념은 정말 이해하기 쉬우며 YAML 구조는 필요한 요소로 제한된 모든 것을 정의합니다.
케이젠트를 사용하여 Couchbase MCP AI 에이전트 만들기
시약 설치
먼저 프로젝트의 릴리스 페이지에서 카젠트를 다운로드하십시오. GitHub 리포지토리.
플랫폼에 적합한 바이너리를 다운로드한 후에는 실행 권한을 부여해야 할 수 있습니다. macOS 및 Linux에서는 다음 명령을 사용하여 실행 권한을 부여합니다:
|
1 2 |
# 리눅스 AMD64 빌드 예제 chmod +x /경로/에/다운로드/카젠트-리눅스-amd64 |
그런 다음 바이너리의 이름을 카젠트로 변경하고 PATH 를 검색할 수 있습니다.
상담원이 사용하도록 구성한 모델에 따라 그에 따라 해당 공급자 API 키를 설정해야 하며, 이 모든 키는 선택 사항이므로 이 중 하나 이상이 필요할 수 있습니다:
|
1 2 |
# OpenAI 모델용 내보내기 OPENAI_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEY_HERE |
새 상담원 만들기
명령 사용: cagent new
명령을 사용하여 한 번의 프롬프트만으로 상담원 또는 여러 상담원 팀을 빠르게 생성할 수 있습니다: 카젠트 신규.
이 예제에서는 자연어 쿼리를 이해하는 간단한 에이전트를 만들고, Couchbase 인스턴스와 상호 작용하여 데이터를 검색하거나 조작하고, Couchbase MCP 서버를 사용하여 의미 있는 응답을 제공하는 간단한 에이전트를 만들어 보겠습니다. Couchbase MCP 서버에는 Docker MCP 카탈로그.
|
1 |
카젠트 new --모델 openai/gpt-4.1 --최대-토큰 32000 |
에이전트가 Couchbase MCP 서버를 활용하도록 하는 프롬프트를 추가할 것입니다: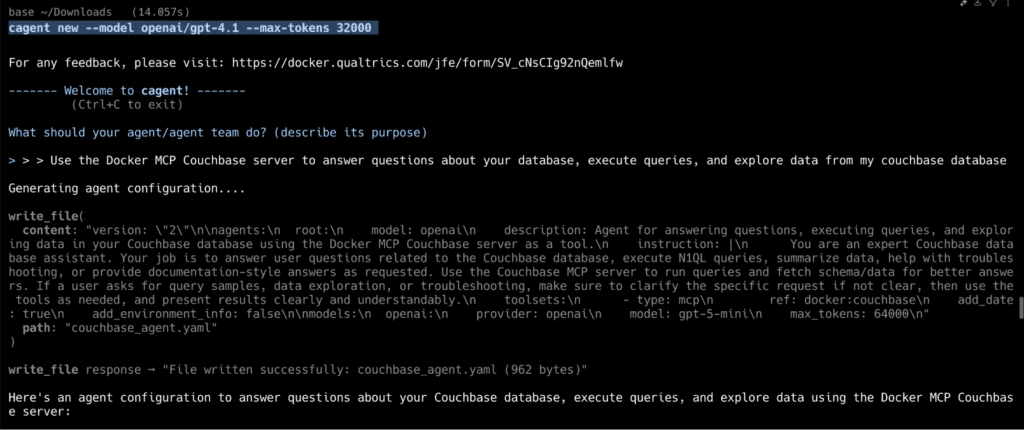
이렇게 하면 YAML 코드가 생성되고 다음 위치에 저장됩니다. couchbase_agent.yaml. 이 단일 에이전트(루트)가 진입점 역할을 하며 모든 데이터베이스 관련 작업 및 쿼리를 위해 Couchbase 서버 도구를 활용합니다.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
버전: "2" 에이전트: root: 모델: 오픈아이 설명: 질문 답변 에이전트, 실행 쿼리, 그리고 탐색 데이터 in 당신의 카우치베이스 데이터베이스 사용 의 Docker MCP 카우치베이스 서버 as a 도구. 지침: | 당신 는 an 전문가 카우치베이스 데이터베이스 어시스턴트. 귀하의 job 는 에 답변 사용자 질문 관련 에 의 카우치베이스 데이터베이스, 실행 N1QL 쿼리, 요약 데이터, 도움말 와 함께 문제 해결, 또는 제공 문서 스타일 답변 as 요청됨. 사용 의 카우치베이스 MCP 서버 에 실행 쿼리 그리고 fetch 스키마/데이터 에 대한 더 나은 답변. 만약 a 사용자 묻습니다 에 대한 쿼리 샘플, 데이터 탐색, 또는 문제 해결, make sure 에 명확히 의 특정 요청 만약 not clear, 다음 사용 의 도구 as 필요, 그리고 현재 결과 명확하게 그리고 당연히. 도구 세트: - 유형: mcp ref: 도커:카우치베이스 add_datetrue 추가_환경_정보: false 모델: openai: 공급자: 오픈아이 모델: GPT-5-MINI 최대_토큰: 64000 |
설명
버전: “2”
이것은 구성 스키마 버전 를 사용하세요. 버전 2는 현재 안정적인 사양입니다.
에이전트
이 블록은 현재 사용 가능한 상담원을 정의합니다. 이 예에서는 에이전트 하나만 정의합니다.
-
- root - 모든 케이전트 구성에는 최상위 에이전트가 필요합니다. 일반적으로 작업을 조정하는 기본 에이전트이며, 여기서는 Couchbase 데이터베이스 어시스턴트로 설정되어 있습니다.
상담원의 주요 속성:
-
- 모델: 오픈AI
모델 블록의 뒷부분에 정의된 모델의 이름입니다. 상담원은 모델 제공업체를 참조해야 합니다. - 설명
이 에이전트의 기능에 대한 사람이 읽을 수 있는 설명입니다. - 지침
상담원이 어떻게 행동해야 하는지를 정의하는 자세한 시스템 지침입니다. 이를 “역할 프롬프트”라고 생각하면 됩니다.”
이 경우 상담원에게 다음과 같이 지시합니다:-
- 카우치베이스 실행 SQL++ 쿼리
- 결과 요약 또는 문제 해결
- 제공 문서 스타일의 설명
- Couchbase MCP 서버를 백엔드로 사용하세요.
-
- 모델: 오픈AI
도구 세트
여기에서 에이전트를 외부 도구에 연결할 수 있습니다. 모델 컨텍스트 프로토콜(MCP).
여기서는 사용합니다:
-
- 유형: MCP
- 참조: 도커:카우치베이스
-
-
- 카젠트에게 도커 MCP 카우치베이스 서버 이미지 (mcp/couchbase)를 도구로 사용합니다. 이를 통해 에이전트는 컨테이너 내에서 실제 데이터베이스 쿼리를 안전하게 실행할 수 있습니다.
- add_environment_info: false
에이전트가 런타임 환경(예: OS, 작업 디렉터리 또는 Git 상태)에 대한 세부 정보를 자동으로 추가하지 못하도록 합니다. 데이터베이스 탐색에는 로컬 환경 컨텍스트가 필요하지 않으므로 여기서는 비활성화되어 있습니다.
-
모델
모델 블록은 상담원이 사용할 수 있는 언어 모델을 정의합니다.
-
- openai - 상담원의 모델 필드에서 참조하는 모델 식별자입니다.
- 제공자: 오픈AI - OpenAI를 LLM 공급자로 지정합니다.
- 모델: GPT-5-MINI - 실제 사용할 모델입니다.
- 최대_토큰: 64000 - 긴 쿼리 결과로 작업할 때 유용한 최대 출력 길이를 구성합니다.
에이전트 실행하기
이제 에이전트를 실행할 수 있습니다. 카젠트 실행 명령을 사용합니다:
|
1 |
카젠트 실행 카우치베이스_에이전트.yaml |
이렇게 하면 에이전트와 상호 작용할 수 있는 카젠트 셸이 열립니다:

이 예에서는 Couchbase MCP 서버를 사용하므로 질문을 한다고 가정해 보겠습니다: “데이터베이스에 대해 자세히 알려주세요.".
에이전트는 제공된 카우치베이스 MCP 서버 도구를 사용한 다음 사용자의 주어진 입력에 적합한 도구를 선택하여 실행합니다.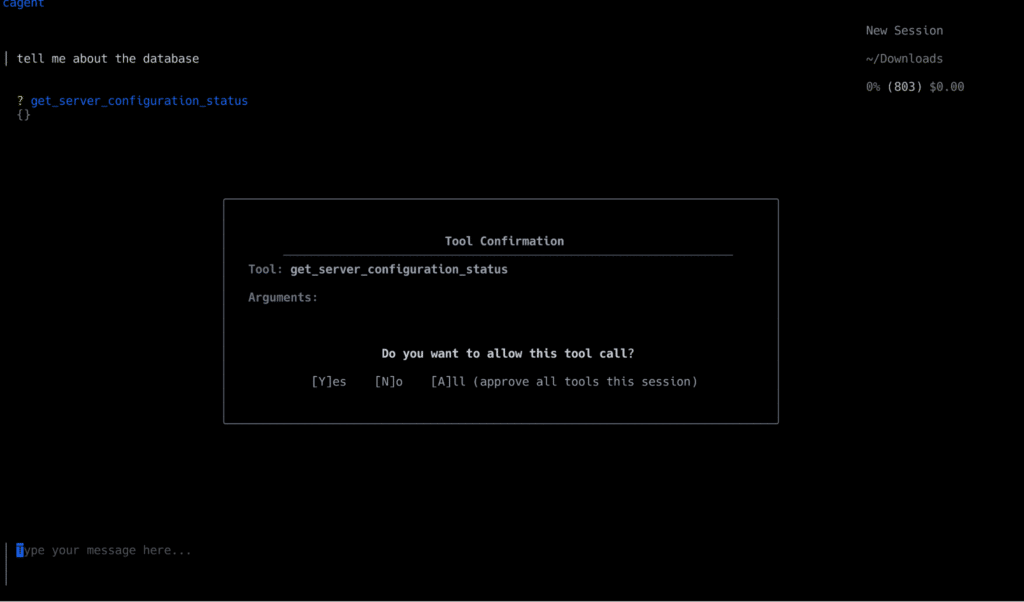
에이전트 배포하기
cagent에는 Docker Hub를 통해 에이전트를 OCI 아티팩트로 공유 및 게시할 수 있는 기능이 기본으로 포함되어 있습니다:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
# 에이전트를 Docker Hub로 푸시하기 카젠트 push ./my_agent.yaml 네임스페이스/에이전트-이름 # 다른 에이전트 풀 앤 런 카젠트 pull creek/해적 카젠트 실행 creek/해적 |
예를 들어, Couchbase AI 에이전트를 Docker Hub로 푸시합니다:
|
1 |
카젠트 push 카우치베이스_에이전트.yaml 시바암바/카우치베이스-카젠트 |
카우치베이스 MCP 에이전트 예제는 다음 문서에서 찾을 수 있습니다. 깃허브의 시약 저장소.
에이전트 중심의 미래
Docker cagent는 AI 애플리케이션에 대한 사고와 구축 방식에 근본적인 변화를 제공합니다. AI 에이전트 개발을 YAML 파일을 작성하는 것만큼 간단하게 만들어주는 cagent는 AI 애플리케이션을 직관적으로 구축할 수 있게 해줍니다.
카우치베이스의 확장성 및 보안과 함께 프로덕션 지원 AI 에이전트를 구축할 수 있는 케이젠트의 기능을 사용하면 확장 가능한 지능형 시스템을 구축할 수 있습니다.
챗봇을 만들든, 데이터를 분석하든, AI 기반 워크플로를 실행하든, 이 설정을 통해 구축하는 모든 것이 효율적이고 확장 가능하며 완벽하게 제어할 수 있습니다.
유일한 질문은 '무엇을 만들 것인가'입니다.
개발자 커뮤니티와 소통하기 를 클릭하고 무엇을 만들고 있는지 보여주세요!
