Category: Application Design

What is Data Modernization? Benefits and Challenges
What is data modernization? This post introduces the concept, explores benefits and challenges, and the role it plays in successful implementation.

Don’t REST – Use a Mobile Database for Apps: Couchbase Webcast Recap
I was recently honored to co-present on a webcast with my colleague and good friend, Aaron LaBeau, Sr. Developer Advocate at Couchbase. Aaron has nearly 30 years of development experience and specializes in building mobile apps, and so seemed the...
Unlocking Next-Level Search: The Power of Vector Databases
Explore vector databases and their role in modern AI and search applications. Understand how they work, their use cases in recommendation systems, and more!

What is a Transactional Database?
What is a transactional database? They are designed to handle the constant, high-volume processing of transactions that occur in businesses.
How to Build Real World Web Applications with Couchbase
I embarked on a journey to build an ASP.NET + Couchbase implementation - a solid starting point for .NET devevelopers using Couchbase

Data Replication: Advantages & Disadvantages
Look at the advantages and disadvantages of data replication. Get all the information you need about incorporating this practice into your business strategy.

5 Reasons to use Molo17 GlueSync for Data Integration
Leveraging GlueSync avoids the need for costly consulting and custom coding. Optimize development resources to focus on more development projects.

What is Modern Application Development? A Guide
Modern application development enables faster, more secure, & flexible software delivery. Learn how modern app development can transform your organization.

What is a Distributed Application? Definition and Examples
Learn what distributed applications are, how to use them, their advantages and disadvantages, and some tools and technologies to build them at Couchbase.
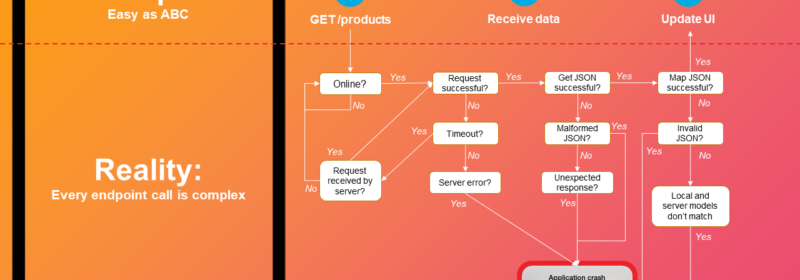
Mobile Developers: Is REST Keeping You Up At Night?
REpresentational State Transfer, commonly known as “REST”, describes a standard for programmatic communication with backend data services over the web. A REST API is a programming interface that uses HTTP requests to POST (create), GET (read), PUT (update), and DELETE...

Implementing an Application Modernization Strategy
What is application modernization? Learn how it can benefit your organization and the steps to implement an application modernization strategy.
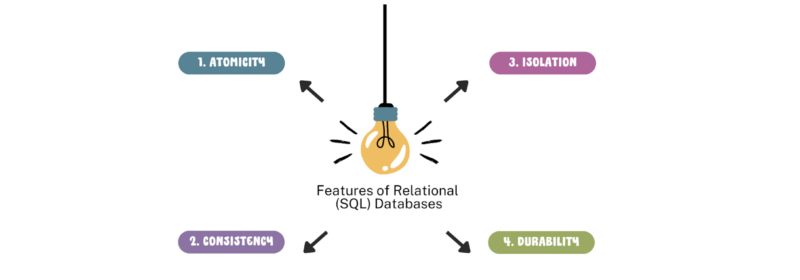
Relational vs. Non-Relational Databases: Features and Benefits
Learn the important features of relational and non-relational databases, their benefits, and when to use them here. Couchbase breaks down the key differences.
Top Posts
- Data Modeling Explained: Conceptual, Physical, Logical
- What are Vector Embeddings?
- What are Embedding Models? An Overview
- Data Analysis Methods: Qualitative vs. Quantitative Techniques
- A Breakdown of Graph RAG vs. Vector RAG
- Application Development Life Cycle (Phases and Management Models)
- Six Types of Data Models (With Examples)
- What Is Data Analysis? Types, Methods, and Tools for Research
- Semantic Search vs. Keyword Search: What’s the Difference?