In this tutorial, we’ll demonstrate how to harness the power of vector search capabilities in Couchbase with n8n’s workflow automation platform. We’ll build a simple travel agent workflow that recommends vacation destinations based on user queries, using vector embeddings to provide contextually relevant results.
Introduction
Vector search makes it possible to search based on semantic similarity rather than exact matches. The Couchbase Search Vector node in n8n allows you to perform vector search operations using Couchbase’s Search Service, supporting retrieval, updating, and insertion of documents in a vector database.
In this tutorial, we’ll:
-
- Set up a Couchbase Capella cluster
- Configure the necessary bucket, scope, and collection
- Create a search index for vector searching
- Build an n8n workflow with data ingestion and chat functionality
- Test our simple travel agent
Prerequisites
-
- An n8n self-hosted instance
- The n8n-nodes-couchbase community node package installed on your n8n instance
- Information on installing community nodes can be found here
- A Couchbase Capella account (free tier is sufficient)
- API keys for OpenAI and Gemini (for embeddings and LLM capabilities)
Step 1: Deploy a Couchbase Cluster
Let’s start by deploying a cluster on Couchbase Capella’s free tier, although any type of cluster with the search service will work.
-
- Log into Couchbase Capella, or sign up for a Couchbase Capella account
- Deploy an Operational Cluster
- The cluster must have the Search service enabled
Step 2: Configure Your Couchbase Database
-
- Create a bucket called travel-agent
- Create a scope within travel-agent called vectors
- Within that scope, create a collection named points-of-interest
Step 3: Create a Search Index
Step 4: Set Up Cluster Access
-
- Create cluster access credentials
- Configure allowed IP addresses
- You must allow the IP address of the machine running n8n
- You can allow access from anywhere for testing purposes, but this should not be used in production scenarios
Step 5: Working with the n8n Workflow
A template of the workflow is provided here. Our n8n workflow consists of two main components:
Data Ingestion Workflow
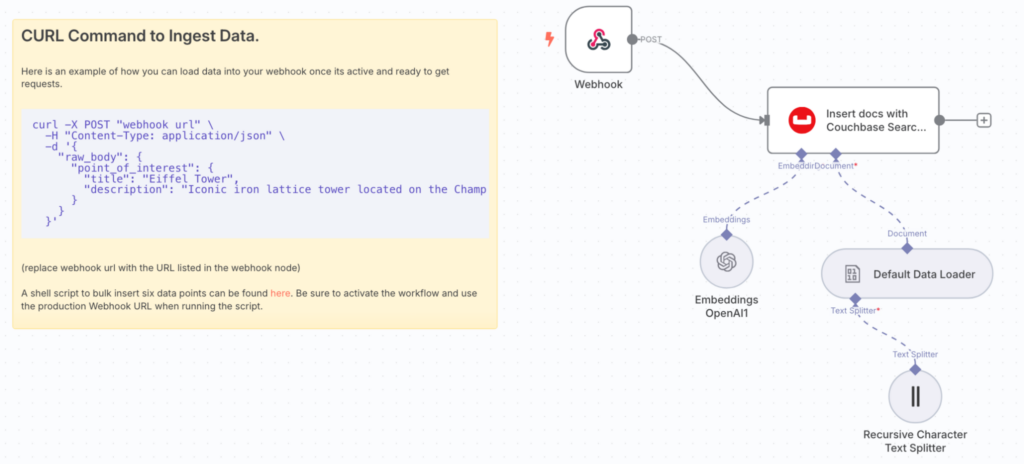
-
- Webhook node (to listen for HTTP requests)
- OpenAI Embeddings node (to generate embeddings on document insertion)
- Note: You’ll need to configure OpenAI credentials for this node
- Couchbase Vector node (configured for document insertion)
- Default Data Loader and Recursive Character Text Splitter
Chat Application Workflow
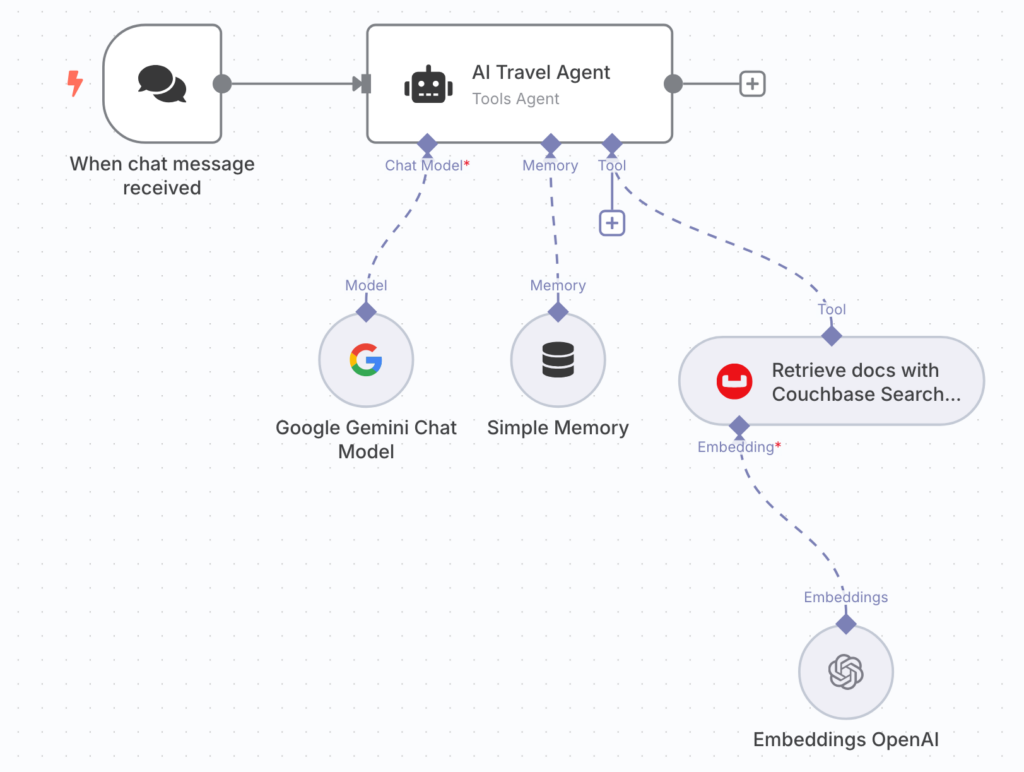
-
- Chat Trigger node
- AI Tools Agent node connect to:
- Gemini (as the Chat Model, for generating responses)
- Note: You will have to configure Gemini credentials for this node
- Simple Memory (as the Memory, to maintain conversation context)
- Couchbase Search Vector node (as the Tool, for search)
- OpenAI Embeddings node (as the Embedding model for the Couchbase Search Vector node, to convert queries to vectors)
- Note: You’ll need to configure OpenAI credentials for this node
- Gemini (as the Chat Model, for generating responses)
Step 6: Configure the Couchbase Vector Nodes
-
- Create a new Couchbase credential with:
- Connection string (from the “Connect” tab in Capella)
- The username and password from your Cluster Access Credentials (created in step 4)
- For both Couchbase Vector nodes, configure the node settings:
- Bucket: travel-agent
- Scope: vectors
- Collection: points-of-interest
- Index: poi-index
- Create a new Couchbase credential with:
Step 7: Ingest Sample Data
We’ll ingest sample travel destination data with descriptions using a provided shell script.
-
- Save and activate your workflow
- Copy the production webhook URL
- Download the provided shell script, and run it to insert a few points of interest:
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
# allow execution of the script chmod +x ./load_poi.sh # run the script, replacing <webhook-url> with the production webhook URL in your workflow ./load_poi.sh <webhook-url> |
The script will create embeddings for each destination description and store them in Couchbase with their vector representations.
Step 8: Test Your Travel Agent
Now you can interact with your travel agent by asking questions like:
-
- “Where should we go for a sightseeing vacation?”
- “I want an adventurous vacation”
- “What’s a good romantic destination?”
The workflow will be:
-
- Convert your query to a vector embedding
- Search Couchbase for semantically similar destinations
- Use the LLM to formulate a response based on the retrieved destination information
Next Steps
While this travel agent may not be super practical for actually planning a vacation, it effectively demonstrates how we can leverage Couchbase and Vector Search to retrieve data from a database and use it in LLM conversations using n8n’s powerful workflow tooling.
Take a look at our Vector Search Cookbook to see examples of other vector search applications in Couchbase for inspiration, and try them out in n8n using the Couchbase Search Vector Node! Happy automating!
