- Products
-
-
Platform
Self-Managed
-
Services
Capabilities
-
-
-
Why Couchbase?
-
-
- Solutions
-
-
By Use Case
-
By industry
-
By Application need
-
-
- Resources
-
-
Popular Docs
-
By Developer Role
-
Quickstart
-
-
- Company
-
-
About
-
Partnerships
-
Our Services
-
Partners: Register a Deal
Ready to register a deal with Couchbase?
Let us know your partner details and more about the prospect you are registering.
Start hereMarriott
Marriott chose Couchbase over MongoDB and Cassandra for their reliable personalized customer experience.
Learn more
-
-
- Pricing
- Try Free
- Sign In
- English
- search
Distributed ACID Transactions in NoSQL Applications
Couchbase provides distributed, multi-document ACID transactions that ensure data consistency, scalability, and high availability across NoSQL applications. Developers can easily build reliable, high-performance transactional systems using Couchbase’s native SDKs, SQL++ support, and seamless integration for cloud, edge, and mobile environments.

Couchbase supports atomic single-document operations and optimistic and pessimistic locking
Distributed multi-document ACID transactions in SQL++
Couchbase supports distributed, multi-document ACID database transactions at scale, without compromising performance or high availability. Migrate your relational database applications to Couchbase to achieve ACID compliance and leverage the power of SQL++ and JSON.
Why choose Couchbase for transactions
Multi-document support
Execute transactions across multiple documents and collections, simplifying complex operations without extra code.
ACID transactions
Get full ACID guarantees – even in distributed environments – so you can focus on building without worrying about data integrity.
Scalable performance
Leverage schemaless data modeling to facilitate easier migration from relational databases.
Seamless integration
Work natively in your preferred Couchbase SDK with intuitive, developer-friendly APIs.
Transactions key capabilities
Couchbase delivers distributed multi-document ACID transactions with full atomicity, consistency, isolation, and durability. Execute complex operations across buckets, scopes, and collections while maintaining high throughput and low latency at scale.
Distributed ACID compliance
Execute multi-document transactions that uphold ACID properties across distributed NoSQL datasets.
Flexible query and key-value operations
Integrate SQL++ queries with key-value operations within a single transaction.
Monotonic atomic view isolation
Ensure that reads within a transaction are consistent with the most recently committed state.
Developer-friendly SDKs
Use SDKs to implement transactions with error handling, retries, and support for asynchronous programming models.
Execute atomic, multi-document writes
Perform all-or-nothing updates across multiple documents and collections within a single, atomic transaction to prevent partial states.
Support high-concurrency workloads
Safely handle simultaneous read and write operations across distributed applications with built-in conflict detection and isolation.

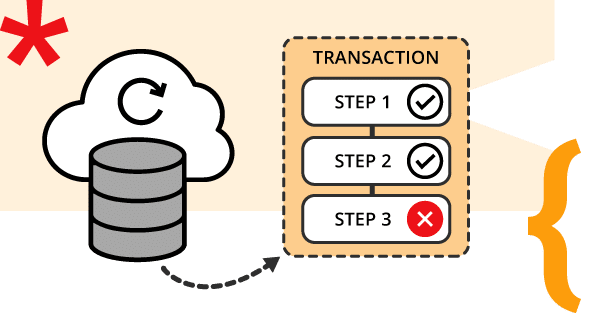
Enable automatic rollback on failure
Leverage transactional guarantees that automatically undo all staged changes if a transaction is interrupted, reducing manual recovery logic.
Run distributed transactions at the edge
Implement ACID-compliant transactions on mobile and edge devices, with offline support and automatic sync when connectivity is restored.

What customers are saying

“Couchbase is a highly scalable, distributed data store that plays a critical role in LinkedIn’s caching systems.”

“What we value a lot is that Couchbase was able to embrace with us our vision to the cloud, and the fact that we wanted to operate data stores directly on PaaS.”
Want to learn more about ACID transactions?
Achieve ACID transactions at scale and get rich SQL support with Couchbase.
Explore related resources

SQL++ support for Couchbase transactions

Create Couchbase transactions with SQL++

Understanding how transactions work in cross data center replications (XDCR)
Start building
Check out our developer portal to explore NoSQL, browse resources, and get started with tutorials.
Use Capella free
Get hands-on with Couchbase in just a few clicks. Capella DBaaS is the easiest and fastest way to get started.
Get in touch
Want to learn more about Couchbase offerings? Let us help.