Couchbase Lite 2.0은 JSON 문서에서 JOIN을 수행할 수 있는 기능을 지원합니다. 이것은 다음을 기반으로 하는 새로운 쿼리 인터페이스의 일부입니다. N1QL는 JSON용 SQL을 확장하는 Couchbase의 선언적 쿼리 언어입니다. SQL에 익숙하다면 새로운 API의 의미를 쉽게 이해할 수 있을 것입니다.
JOIN을 사용하면 여러 문서의 콘텐츠를 결합할 수 있습니다. 이 게시물에서는 Couchbase Lite에서 가능한 JOIN의 유형을 설명하기 위해 예제를 제공합니다. 각 쿼리에 대해 해당하는 SQL 쿼리를 제공합니다. 이 블로그는 새로운 쿼리 API의 기본 사항에 익숙하다고 가정하므로, 아직 숙지하지 않은 경우 반드시 이전 게시물 를 먼저 읽어 보세요. 관심이 있으시다면 이 글의 끝에 쿼리 인터페이스의 다른 기능에 대해 설명하는 블로그 링크가 제공됩니다.
최신 Couchbase Mobile 2.0 사전 릴리스 빌드는 다음에서 다운로드할 수 있습니다. 다운로드 페이지로 이동합니다.
배경
1.x 버전의 Couchbase Mobile을 사용 중이라면 다음과 같은 내용을 잘 알고 계실 것입니다. 맵 보기 를 사용하여 인덱스와 쿼리를 만들 수 있습니다. 2.0에서는 더 이상 뷰와 맵 함수를 만들 필요가 없습니다! 대신, 간단한 인터페이스를 통해 인덱스를 생성하고 쿼리 빌더 인터페이스를 사용해 쿼리를 구성할 수 있습니다. 새로운 쿼리 인터페이스는 사용하기 더 간단하고 훨씬 더 강력합니다. 이 글에서 몇 가지 기능을 살펴보겠습니다.
샘플 프로젝트
여기서 설명하는 예제에서는 iOS용 Swift를 사용하지만, 동일한 쿼리 인터페이스는 Android 및 Windows 플랫폼에서도 지원됩니다.
따라서 약간의 수정만 하면 다른 플랫폼에서 작업할 때 이 글의 쿼리 예제를 재사용할 수 있습니다.
샘플 Swift 프로젝트에 관심이 있다면 아래 지침을 따르세요.
- GitHub에서 iOS Swift 플레이그라운드 복제하기
|
1 |
$ git clone https://github.com/couchbaselabs/couchbase-lite-ios-api-playground |
- 해당 항목의 설치 지침을 따르세요. README 파일을 사용하여 플레이그라운드를 빌드하고 실행합니다.
샘플 데이터 모델
다음 위치에 있는 샘플 데이터베이스를 사용합니다. 여기. 이 사전 구축된 데이터베이스를 모바일 애플리케이션에 임베드하여 쿼리에 사용할 수 있습니다.
샘플 데이터 세트는 약간 인위적이지만 여기서는 다음과 같은 몇 가지 일반적인 사용 사례를 보여주기 위한 것입니다. join 쿼리.
- "직원" 유형 문서
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
{ "type": "employee", "firstname": "John", "lastname": "Smith", "department": "1000", "location": "101" } |
- "부서" 유형 문서
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
{ "type": "department", "name": "Product Management", "code": "2000", "head": { "firstname": "Patricia", "lastname": "Shoji" }, "location":["101","102"] } |
- "위치" 유형 문서
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
{ "type": "location", "name": "HQ", "address": "1123 6th St. Melbourne, FL 32904 ", "code": "101" } |
** 아래의 각 쿼리 예제는 위의 모델을 참조하세요. **
데이터베이스 핸들
아래 쿼리에서는 다음과 같이 데이터베이스 API를 사용하여 CouchbaseLite 데이터베이스를 열거나 생성합니다.
|
1 2 |
let options = DatabaseConfiguration() let db = try Database(name: kDBName, config: options) |
색인
읽기 쿼리 속도를 높이려면 쿼리할 속성에 인덱스를 만들면 됩니다. 대규모 데이터 세트에서 성능 향상은 상당할 것입니다. 물론 인덱스를 저장하기 위해 필요한 스토리지가 증가하고 쓰기 성능에도 영향을 미칠 수 있다는 점에 유의하세요. 따라서 너무 많은 인덱스를 만들지 않도록 주의하세요.
다음 예제에서는 ValueIndex 에서 유형 문서의 속성
|
1 |
try db.createIndex(IndexBuilder.valueIndex(items: ValueIndexItem.property("type")),withName: "typeIndex") |
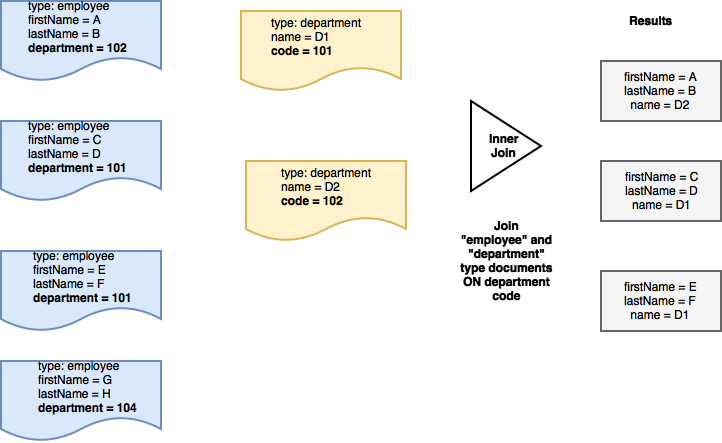
조인 또는 내부 조인
두 문서 모두에 지정된 조건을 충족하는 경우에만 간단한 조인 또는 내부 조인 쿼리를 사용하여 참여 문서에서 속성을 가져올 수 있습니다. 켜기 절을 사용합니다.
예를 들어 앞서 제시한 데이터 모델을 고려할 때, 다음과 같은 데이터 모델을 가져오고 싶다고 가정해 보겠습니다. 이름, 성 "직원"과 해당 이름 직원이 소속된 '부서'의 이름입니다. 이 경우 이름 그리고 성 의 문서에서 프로퍼티를 가져옵니다. 유형 "직원" 및 부서 이름 의 문서에서 가져옵니다. 유형 "부서"에 해당하는 경우에만 부서 속성은 "직원"의 해당 속성과 일치하는 코드 속성을 "부서"
즉, '부서'와 일치하는 문서가 없는 경우 코드 를 '직원' 문서에 입력하면 해당 직원의 세부 정보가 출력 결과에 포함되지 않습니다.
요청
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
try db.createIndex(IndexBuilder.valueIndex(items: ValueIndexItem.property("type")),withName: "typeIndex") // set up aliases to represent the data source for "department" type document let departmentDS = DataSource.database(db).as("departmentDS") // Property expression for "department" (in employee documents) let employeeDeptExpr = Expression.property("department").from("employeeDS") // Property expression for "code" (in department documents) let departmentCodeExpr = Expression.property("code").from("departmentDS") // Join clause: Join employee type and department type documents where the // "department" field of employee documents is equal to the department "code"; // of "department" documents let joinExpr = employeeDeptExpr.equalTo(departmentCodeExpr) .and(Expression.property("type").from("employeeDS").equalTo(Expression.string("employee"))) .and(Expression.property("type").from("departmentDS").equalTo(Expression.string("department"))) // Construct inner join expression with ON query. let join = Join.join(departmentDS).on(joinExpr) // return the "firstname", "lastname"; and "department"; name from the documents that are joined based // on the JOIN expression let searchQuery = Query.select( SelectResult.expression(Expression.property("firstname").from("employeeDS")), SelectResult.expression(Expression.property("lastname").from("employeeDS")), SelectResult.expression(Expression.property("name").from("departmentDS"))) .from(employeeDS) .join(join) |
ANSI SQL
위 쿼리에 해당하는 SQL 문은 다음과 같습니다.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
SELECT employeeDS.firstname, employeeDS.lastname, departmentDS.name FROM `travel-sample` employeeDS INNER JOIN `travel-sample` departmentDS ON employeeDS.department = departmentDS.code WHERE employeeDS.type = "employee" AND departmentDS.type = "department" |
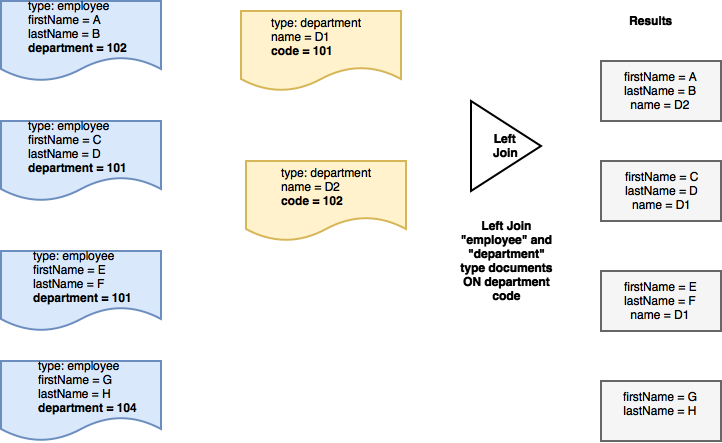
왼쪽 조인 또는 왼쪽 외부 조인
두 문서가 모두 지정된 조건을 충족하는 경우 왼쪽 조인 쿼리를 사용하여 참여 문서에서 속성을 가져올 수 있습니다. 켜기 절을 사용합니다. 그러나 일반 조인과 달리 결과에는 일치하지 않는 문서가 왼쪽에 있는 켜기 절을 사용합니다.
예를 들어 앞서 제시한 데이터 모델을 고려할 때, 다음과 같은 데이터 모델을 가져오고 싶다고 가정해 보겠습니다. 이름, 성 "직원"과 해당 이름 직원이 소속된 '부서'의 이름입니다.
또한 다음과 같은 경우에도 관심이 있다고 가정해 보겠습니다.이름 그리고 성 "직원"의 부서 코드가 수행하는 작업 not 는 유효한 부서에 해당합니다. 예를 들어 다음과 같은 경우에 해당할 수 있습니다. 부서 직원의 코드가 잘못 입력되었습니다.
이 경우 이름 그리고 성 의 문서에서 프로퍼티를 가져옵니다. 유형 "직원" 및 부서 이름 의 문서에서 가져옵니다. 유형 "부서"인 경우 부서 속성은 "직원"의 해당 속성과 일치하는 코드 속성을 추가합니다.
일치하는 부서가 없는 경우에는 이름 그리고 성 속성이 반환됩니다.
요청
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
// set up aliases to represent the data source for "employee" type document let employeeDS = DataSource.database(db).as("employeeDS") // set up aliases to represent the data source for "department" type document let departmentDS = DataSource.database(db).as("departmentDS") // Property expression for "department" (in employee documents) let employeeDeptExpr = Expression.property("department").from("employeeDS") // Property expression for "code" (in department documents) let departmentCodeExpr = Expression.property("code").from("departmentDS") // Join clause: Join department type and employee type documents where the // "department" field of employee documents is equal to the department "code" of // "department" documents let joinExpr = employeeDeptExpr.equalTo(departmentCodeExpr) .and(Expression.property("type").from("employeeDS").equalTo(Expression.string("employee"))) .and(Expression.property("type").from("departmentDS").equalTo(Expression.string("department"))) // join expression with ON query let join = Join.leftJoin(departmentDS).on(joinExpr) // return the "firstname", "lastname" and "department" name from the documents that are joined based on the JOIN expression let searchQuery = Query.select( SelectResult.expression(Expression.property("firstname").from("employeeDS")), SelectResult.expression(Expression.property("lastname").from("employeeDS")), SelectResult.expression(Expression.property("name").from("departmentDS"))) .from(employeeDS) .join(join) |
ANSI SQL
위 쿼리에 해당하는 SQL 문은 다음과 같습니다.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
SELECT employeeDS.firstname, employeeDS.lastname, departmentDS.name FROM `travel-sample` employeeDS LEFT JOIN `travel-sample` departmentDS ON employeeDS.department = departmentDS.code WHERE employeeDS.type = "employee" AND departmentDS.type = "department" |
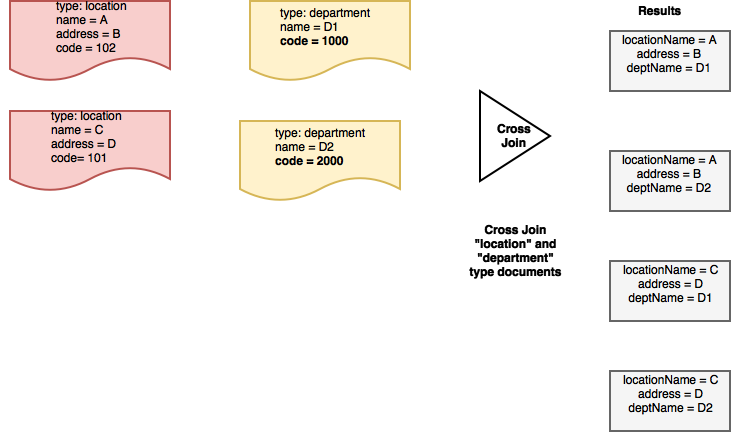
교차 가입
교차 JOIN 쿼리를 사용하여 참여 문서에서 속성의 직교곱을 가져올 수 있으며, 일반적으로 문서는 서로 관련이 없습니다. 이것은 내부 JOIN과 동일합니다. 없이 의 켜기 절을 사용합니다.
예를 들어, 앞서 제시한 데이터 모델을 고려하여 다음과 같은 모든 문서의 직교곱을 가져오고 싶다고 가정해 보겠습니다. 유형 "위치" 및 유형 "부서". 즉, 모든 "위치" 유형 문서가 각 "부서"와 결합됩니다. 유형 문서.
따라서 on 절을 포함하는 경우, 교차 조인 표현식에 지정된 어디 절을 사용하여 문서에 따라 고려할 문서의 하위 집합을 필터링합니다. 유형.
요청
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
// set up aliases to represent the data source for "department" type document let departmentDS = DataSource.database(db).as("departmentDS") // set up aliases to represent the data source for "location" type document let locationDS = DataSource.database(db).as("locationDS") // Property expression for "department" (in employee documents) let employeeDeptExpr = Expression.property("code").from("departmentDS") // Property expression for "department" (in location documents) let departmentCodeExpr = Expression.property("code").from("locationDS") // cross join expression let join = Join.crossJoin(locationDS) // type property expressions let deptTypeExpr = Expression.property("type").from("departmentDS") let locationTypeExpr = Expression.property("type").from("locationDS") // The where clauses filters the set of documents to cross-join on // We alias the "code" properties since it exists in both the department and location docs // NOTE: The where clause is used to filter the documents to be considered as // part of the cartesian join let searchQuery = Query.select( SelectResult.expression(Expression.property("name").from("departmentDS")).as("DeptName"), SelectResult.expression(Expression.property("name").from("locationDS")).as("LocationName"), SelectResult.expression(Expression.property("address").from("locationDS"))) .from(departmentDS) .join(join) .where(deptTypeExpr.equalTo(Expression.string("department")) .and(locationTypeExpr.equalTo(Expression.string("location")))) |
ANSI SQL
위 쿼리에 해당하는 SQL 문은 다음과 같습니다.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
SELECT departmentDS.name AS DeptName, locationDS.name AS LocationName, locationDS.address FROM `travel-sample` departmentDS CROSS JOIN `travel-sample` locationDS WHERE departmentDS.type = "department" |
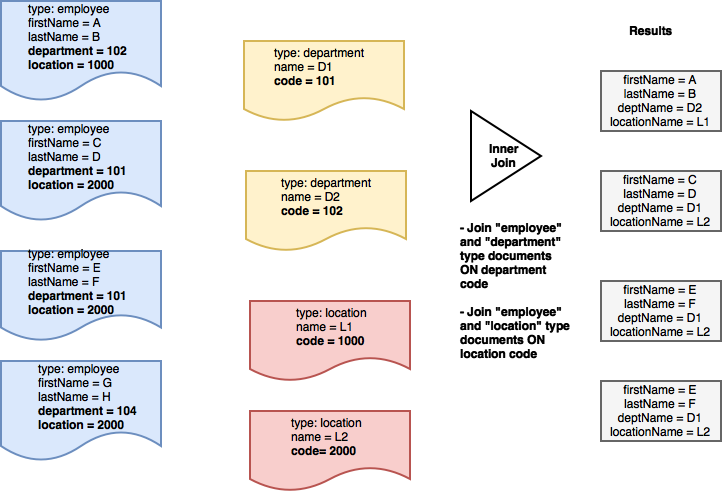
조인 연결
여러 JOIN 표현식을 지정할 수 있습니다. 선택 절을 추가하여 다양한 기준에 따라 문서 간에 조인할 수 있도록 합니다.
예를 들어 앞서 제시한 데이터 모델을 고려할 때, 다음과 같은 데이터 모델을 가져오고 싶다고 가정해 보겠습니다. 이름, 성 "직원"과 해당 이름 을 사용하여 직원이 소속된 '부서'를 확인할 수 있습니다. 또한 직원이 속한 이름 직원이 근무했던 '위치'를 입력합니다.
이 경우 두 개의 JOIN 표현식을 사용합니다.
첫 번째 JOIN 표현식은 다음과 같은 문서를 조인하는 데 사용됩니다. 유형 "직원"은 다음 문서와 함께 유형 "부서 코드" 속성을 기반으로 "부서"를 설정합니다. 이 경우 이름 그리고 성 의 문서에서 프로퍼티를 가져옵니다. 유형 "직원" 및 부서 이름 의 문서에서 가져옵니다. 유형 "부서"에 해당하는 경우에만 부서 속성은 "직원"의 해당 속성과 일치하는 코드 속성을 추가합니다.
두 번째 JOIN 표현식은 다음과 같은 문서를 조인하는 데 사용됩니다. 유형 "직원"은 다음 문서와 함께 유형 "위치 코드" 속성을 기반으로 "위치"를 설정합니다. 이 경우 이름 그리고 성 의 문서에서 프로퍼티를 가져옵니다. 유형 "직원" 및 위치 이름 의 문서에서 가져옵니다. 유형 "위치"에 해당하는 경우에만 위치 속성은 "직원"의 해당 속성과 일치하는 코드 속성을 추가합니다.
요청
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 |
// set up aliases to represent the data source for "employee" type document let employeeDS = DataSource.database(db).as("employeeDS") // set up aliases to represent the data source for "department" type document let departmentDS = DataSource.database(db).as("departmentDS") // set up aliases to represent the data source for "location" type document let locationDS = DataSource.database(db).as("locationDS") // Property expression for "department" property (in employee documents) let employeeDeptExpr = Expression.property("department").from("employeeDS") // Property expression for "location" property (in employee documents) let employeeLocationExpr = Expression.property("location").from("employeeDS") // Property expression for "code" property (in department documents) let departmentCodeExpr = Expression.property("code").from("departmentDS") // Property expression for "code" property (in location documents) let locationCodeExpr = Expression.property("code").from("locationDS") // Join Criteria 1 // Join where the "department" field of employee documents is equal to the department "code" of "department" documents let joinDeptCodeExpr = employeeDeptExpr.equalTo(departmentCodeExpr) .and(Expression.property("type").from("employeeDS").equalTo(Expression.string("employee"))) .and(Expression.property("type").from("departmentDS").equalTo(Expression.string("department"))) // Join Criteria 2 // Join where the "department" field of employee documents is equal to the department "code" of "department" documents let joinLocationCodeExpr = employeeLocationExpr.equalTo(locationCodeExpr) .and(Expression.property("type").from("employeeDS").equalTo(Expression.string("employee"))) .and(Expression.property("type").from("locationDS").equalTo(Expression.string("location"))) // join expression for department code let joinDeptCode = Join.join(departmentDS).on(joinDeptCodeExpr) // join expression for location code let joinLocationCode = Join.join(locationDS).on(joinLocationCodeExpr) // Multiple join expressions in the join clause let searchQuery = QueryBuilder.select(SelectResult.expression(Expression.property("firstname").from("employeeDS")), SelectResult.expression(Expression.property("lastname").from("employeeDS")), SelectResult.expression(Expression.property("name").from("departmentDS")).as("deptName"), SelectResult.expression(Expression.property("name").from("locationDS")).as("locationName")) .from(employeeDS) .join(joinDeptCode,joinLocationCode) |
ANSI SQL
위 쿼리에 해당하는 SQL 문은 다음과 같습니다.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 |
SELECT employeeDS.firstname, employeeDS.lastname, departmentDS.name AS deptName, locationDS.name AS locationName FROM `travel-sample` employeeDS JOIN `travel-sample` departmentDS ON employeeDS.department = departmentDS.code JOIN `travel-sample` locationDS ON employeeDS.location = locationDS.code WHERE departmentDS.type = "department" AND locationDS.type = "location" AND employeeDS.type = "employee" |
함수를 사용한 조인 표현식
모든 예제에서 equalTo 비교를 사용하는 경우, 다음과 같은 비교 연산자를 사용할 수 있다는 점에 유의해야 합니다. 사이, 보다 크거나 같음 등을 JOIN 표현식에 포함할 수 있습니다. 또한 유효한 기능 표현식을 사용할 수 있습니다. 이것은 강력한 기능입니다.
예를 들어, 앞서 제시한 데이터 모델을 고려하여 부서에서 이름 및 해당 위치 부서가 위치한 '위치'의 이름입니다. 부서는 하나 이상의 위치에 속할 수 있습니다.
이 경우 JOIN 표현식은 "부서" 및 "위치" 유형 문서를 조인하여 위치 배열 속성을 사용하여 부서 문서의 배열 함수 표현식입니다.
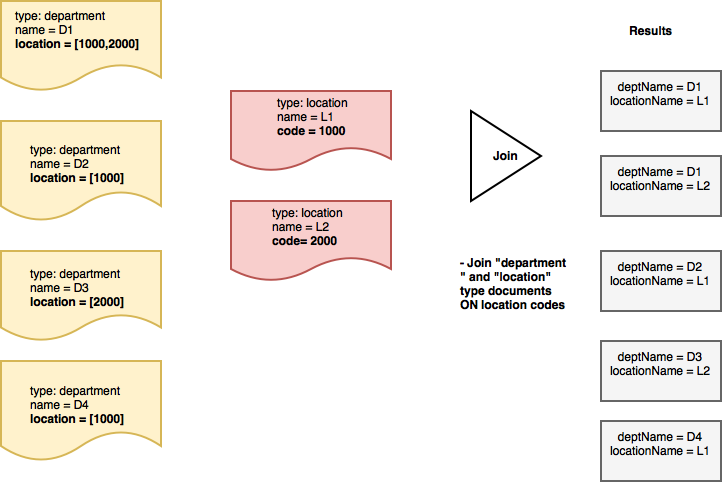
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 |
// set up aliases to represent the data source for "department" type document let departmentDS = DataSource.database(db).as("departmentDS") // set up aliases to represent the data source for "location" type document let locationDS = DataSource.database(db).as("locationDS") // Property expression for "location" property (in department documents) let departmentLocationExpr = Expression.property("location").from("departmentDS") // Property expression for "code" property (in location documents) let locationCodeExpr = Expression.property("code").from("locationDS") // Join where the "code" field of location documents is contained in // the "location" array of "department" documents let joinDeptCodeExpr = ArrayFunction.contains(departmentLocationExpr, value: locationCodeExpr) .and(Expression.property("type").from("locationDS").equalTo(Expression.string("location")) .and(Expression.property("type").from("departmentDS").equalTo(Expression.string("department")))) // join expression let joinLocationCode = Join.join(departmentDS).on(joinDeptCodeExpr) // Search query with JOIN let searchQuery = QueryBuilder.select( SelectResult.expression(Expression.property("name").from("departmentDS")).as("departmentName"), SelectResult.expression(Expression.property("name").from("locationDS")).as("locationName")) .from(locationDS) .join(joinLocationCode) |
ANSI SQL
SQL에서는 배열이 지원되지 않습니다. 그러나 N1QL에는 배열이 지원됩니다. 위 쿼리에 해당하는 SQL과 유사한 문은 다음과 같습니다.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
SELECT departmentDS.name AS departmentName, locationDS.name AS locationName FROM `travel-sample` locationDS JOIN `travel-sample` departmentDS ON ANY code IN departmentDS.location SATISFIES code = locationDS.location END WHERE departmentDS.type = "department" AND locationDS.type = "location" |
다음 단계
이 블로그 게시물에서는 여러 JSON 문서의 결과를 결합할 수 있는 Couchbase Mobile 2.0의 강력한 JOIN 기능에 대해 살펴봅니다. 다음을 수행할 수 있습니다. 다운로드 카우치베이스 모바일 2.0을 설치하고 이 게시물에서 설명한 쿼리를 테스트해 보세요. 이것은 시작에 불과합니다. 향후 릴리스에서 더 많은 기능이 추가될 예정입니다.
다음은 관심을 가질 만한 몇 가지 다른 Couchbase 모바일 쿼리 관련 게시물입니다.
- 이 블로그 게시물 기본 사항에 대해 설명합니다.
- 이 블로그 게시물 배열 컬렉션을 쿼리하는 방법에 대해 설명합니다.
- 이 블로그 게시물 에서는 전체 텍스트 검색(FTS) 기능에 대해 설명합니다.
질문이나 피드백이 있으면 아래에 댓글을 남기거나 트위터로 언제든지 문의해 주세요. @rajagp 또는 이메일을 보내주세요. priya.rajagopal@couchbase.com. . 카우치베이스 포럼 를 통해 질문할 수 있습니다.