FEATURES
Key features of Couchbase vs. MongoDB
- What’s included
- JSON flexibility
- Built-in cache for millisecond responses at scale
- Semantic cache for LLMs
- Native vector search, cloud, and on-prem
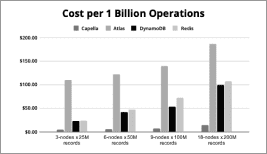
- Billion-scale vector search
- AI model hosting with NVIDIA
- Built-in RAG pipeline automation
- Mobile, edge, and peer-to-peer sync
- SQL++
- Native full-text search
- XDCR master-master replication
- Automatic sharding
- Masterless shared-nothing architecture
- ACID transactions
- Multi-dimensional scaling
- Vector search on mobile
- Real-time analytics engine
- Multisource, zero-ETL ingestion
- Write-back, real-time analytics to source cluster
- Couchbase
- MongoDB
- BSON
- Lucene-based and only available in Atlas
Code snippet
Comparison of equivalent queries in Couchbase SQL++ and MongoDB's MQL
/* equivalent to the Mongo example */
SELECT SUM(value * volume) AS val, symbol
FROM db.stocks
WHERE symbol IN ( "AAPL", "GOOG" ) AND value > 0
GROUP BY symbol
ORDER BY val DESC, symbol ASC// equivalent to the SQL++ example
db.stocks.aggregate([
{ "$match": {
"$and": [
{"symbol": {
"$in": [
"AAPL",
"GOOG"]}},
{ "value": {
"$gt": 0 }}]}},
{ "$group": {
"_id": {
"symbol": "$symbol" },
"sum(value * volume)": {
"$sum": {
"$multiply": [
"$value",
"$volume"]}}}},
{ "$project": {
"_id": 0,
"sum(value * volume)": "$sum(value * volume)",
"symbol": "$_id.symbol"}}
{ "$sort": {
"sum(value * volume)": -1,
"symbol": 1 }}]})CUSTOMERS
What customers are saying
-
“We see very consistent 500 microsecond response times from Couchbase even at very large scale.”
Technical Lead, Cisco100B+ user sessions per year500 microsecond response times -
"We found that the replication technology across data centers for Couchbase was superior, especially for large workloads."
Claus Moldt, CIO, FICO<1 ms response times24x365 application uptime -
“With less than half the servers, we can increase performance and gain a much better scalable architecture.”
Amir Ish-Shalom, Sr. Director of Operations, Viber15 billion call and message events/day60% reduction in total servers